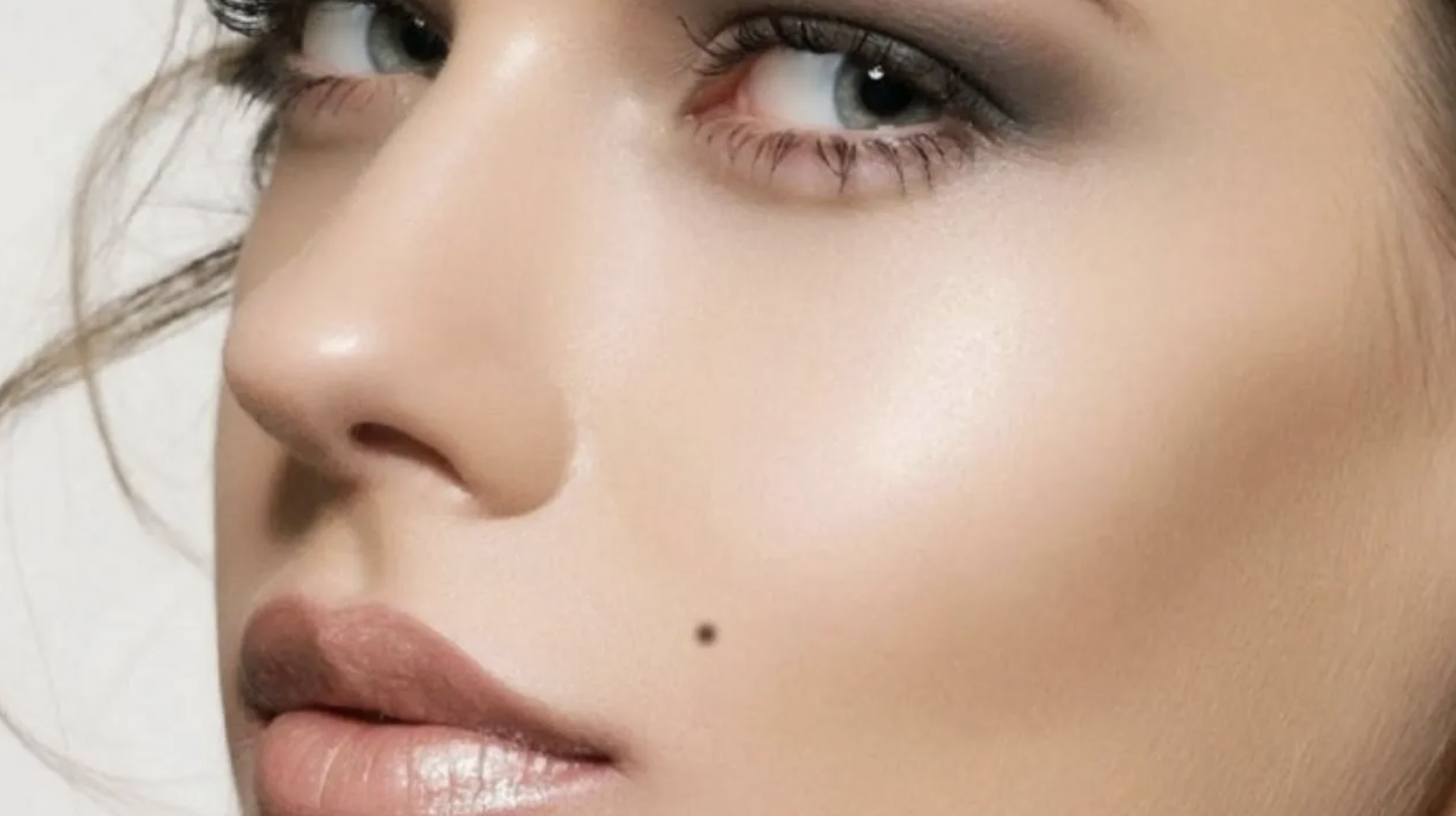
What are moles?
All people have large and small moles, aka nevus, over their bodies. What are these moles? NHS and dermatologists indicate that all normal skin has melanocytes. A melanocyte can produce melanin, which scatters around the body. These melanin are sent to 20 to 30 neighbouring epidermal cells. A mole on the skin is basically a mass of melanocytes clustered. Sometimes the colour is brown or beige, and sometimes it is the usual black.
The majority of moles are benign, which are not expected to develop into cancer, and normally appear on the body before the age of 20. For this reason, it does not cause any discomfort. Moles can undergo some mild changes in the same way that creatures can grow and transform. There are possible variations of the following:
- Moles all over the body changes jointly: This situation typically happens in puberty or during pregnancy. In some, the moles may be affected when they take medication or chemotherapy in a long term.
- Local changes in the mole: Areas that are susceptible to sunlight, such as several moles on the hands, can turn black together. If it is getting worse, they even cause skin disorders.
- The transition of a single mole: Moles also contain hair follicles and may suffer from folliculitis. If it is accompanied by an epidermoid cyst, it is likely to cause inflammation and infection.
Types of moles
The real cause of the moles is still unknown. The majority of experts believe that moles are more genetically related. Secondly, moles are more common on skin that has been exposed to the sun. The skin is composed of three layers: epidermis, dermis and subcutaneous tissue. On the other hand, there are three kinds of moles divided by the shade of colour, which can generally be judged by the bare eye:
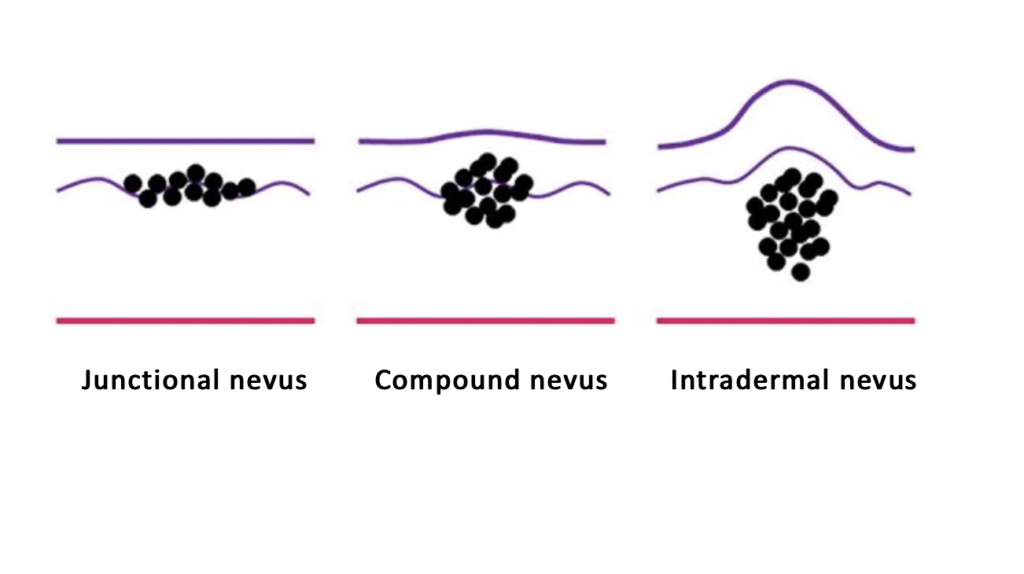
- Junctional nevus: Nevus are found between the epidermis and the dermis. They are actually within the epidermis and are usually small and flat. The surface appears to be a flat black spot, which is what we commonly know as a mole.
- Compound nevus: In addition to the epidermis, the number of nevus cells increases in the dermis, and the nevus then starts to bulge out slightly.
- Intradermal nevus: Mole growth only occurs in the dermis. The colour of the mole at this point is rarely so dark but is most likely to be a light brown or even skin-coloured bump. Most Intradermal nevus are hemispherical that seems to be protruding from the skin. In general, the bigger size and more hair is Intradermal nevus
Which moles should be removed?
NHS suggests that If a mole persists for more than a few weeks, it is important to monitor your skin carefully for new moles and the condition of the original one:
- The shape of the mole has transformed and felt bumpy and irregular.
- Colours shift, shade may become darker, or more than two colours were produced.
- A scratching sensation or crusting or bleeding in that area.
- Very obvious skin bulges and moles have grown substantially larger.
If you are experiencing these conditions, it is suggested that you reserve an appointment with your GP to check if there are any other skin disorders that may happen.
Melanoma
Melanoma is a relatively rare but highly invasive type of skin cancer that originates in melanocytes. Melanocytes are responsible for the production of melanin, which protects the body from external damage caused by ultraviolet (UV) radiation.
If you notice any unusual changes in your mole after the above observations, you should consult your GP as soon as possible. If there are any genuine concerns, you will be referred to a dermatologist. The dermatologist will collect tissue samples from moles for testing. If the test result is melanoma, then the area is already cancerous. The treatment typically involves surgical excision.
NHS is advising the public to prevent the development of melanoma by keeping them from exposure to the sun. The UV of the sun can cause an increased risk of cancer and sunscreen is essential for outdoor activities.
The sun protection expert, Supergoop!, Everyday Sunscreen With Cellular Response Technology Spf 50 is the most popular sunscreen product all over the world. Everyday Sunscreen contains easily absorbs formula, which allows the skin to breathe and sweat. Ingredients are extracted from citrus, basil and boise de rose. Everyone can have their subtle sensorial experience with no unpleasant “sunscreen” smell.

We believe that everyone has bought Sunbum’s Face Lotion SPF 50 before. It is designed for daily use. You will feel weightless as it will quickly absorb into your skin. Moreover, Sunbum’s Face Lotion is not just for your face, but also is allowing you to apply it to the whole body. Sun Bum sunscreens are tested, approved, and recommended by The Skin Cancer Foundation (SCF). Both sunscreen you can easily purchase in the link.

Check out our recommended products for your face and body.
Disclaimer: NUWA BeautyLab is an information sharing and amazon affiliate website, none of the team members is a doctor or any medical professional. Any information including but not limited to text, graphics, and images, is used for information sharing purposes only. None of the advice or treatments found on this website can be used as a substitute for professional medical advice. It is suggested to seek a medical professional if you have any concerns regarding any health and well-being issues.